 Diffusion Phase Diagram
Diffusion Phase DiagramAbstract
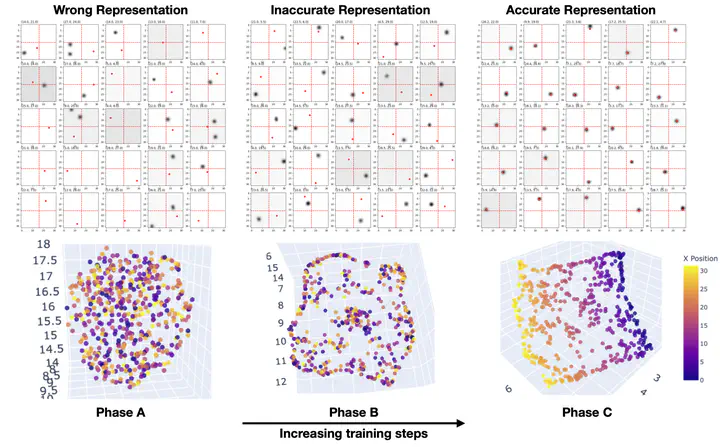
Diffusion models are capable of impressive feats of image generation with uncommon juxtapositions such as astronauts riding horses on the moon with properly placed shadows. These outputs indicate the ability to perform compositional generalization, but how do the models do so? We perform controlled experiments on conditional DDPMs learning to generate 2D spherical Gaussian bumps centered at specified x- and y-positions. Our results show that the emergence of semantically meaningful latent representations is key to achieving high performance. En route to successful performance over learning, the model traverses three distinct phases of latent representations: (phase A) no latent structure, (phase B) a 2D manifold of disordered states, and (phase C) a 2D ordered manifold. Corresponding to each of these phases, we identify qualitatively different generation behaviors: 1) multiple bumps are generated, 2) one bump is generated but at inaccurate x and y locations, 3) a bump is generated at the correct x and y location. Furthermore, we show that even under imbalanced datasets where features (x- versus y-positions) are represented with skewed frequencies, the learning process for x and y is coupled rather than factorized, demonstrating that simple vanilla-flavored diffusion models cannot learn efficient representations in which localization in x and y are factorized into separate 1D tasks. These findings suggest the need for future work to find inductive biases that will push generative models to discover and exploit factorizable independent structures in their inputs, which will be required to vault these models into more data-efficient regimes.